OKRs itu Apa Sebenarnya?
Kenapa pakai OKRs?
Bagaimana perusahaan set goal saat ini? Apa saja kendala dengan cara tersebut?
PERFORMANCE
ENGAGEMENT
ALIGNMENT & CONNECTION
PRIORITIZATION & DISCIPLINE
COMMUNICATION
Ketika kita buat goal yang mau kita capai, performa kita pasti lebih meningkat.
Meningkatkan engagement dalam mencapai goal perusahaan.
Ketika perusahaan tahu apa fokusnya dan bagaimana mengukur pencapaian atas goal yang telah dibuat, akan lebih mudah bagi individu untuk mengarahkan projek mereka dengan goal perusahaan.
Menghubungkan obyektif perusahaan, tim dan individu sehingga semuanya bekerjasama untuk satu tujuan yang sama.
Kadang sulit untuk tim untuk menolak ide/projek yang bagus, tapi ketika semuanya sudah setuju dengan objektif mana yang paling penting, akan jadi lebih mudah untuk menunda ide-ide yang prioritasnya rendah, jadi perusahaan ada kedisiplinan dan respon tegas terhadap komitmen yang sudah dibuat/prioritaskan.
Dengan OKRs, perusahaan bisa komunikasikan prioritas dan tetap mengarah ke goal yang mau dicapai.
Setiap individu tahu apa yang diharapkan oleh tim dan sebaliknya.
Apa itu OKRs?
Objectives & Key Results: goal setting framework yang dipakai oleh banyak startups dan established business.
Untuk menjawab dua pertanyaan berikut:
Kemana tujuan kita? Itulah objectives.
Apa tolak ukur kita terhadap tujuan kita? Itulah key results.
Objectives harus ambisius dan kadang terasa kurang nyaman makanya sering disebut juga stretch goals.
Agak tricky karna ada anggapan sengaja merencanakan tim untuk gagal, tapi sebenarnya ketika kita aim high, goal yang gagal pun sering menghasilkan pencapaian yang substantial.
Kuncinya adalah komunikasikan stretch goals dan tolak ukur kita ata goal tersebut.
Objectives harus SMART (Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, Time-bound)
Progress update (bukan assessment) harus dilakukan setiap minggu supaya real-time.
Key Results harus terukur dan mudah dinilai dengan angka (misalnya skala 0–1.0).
OKRs harus transparan dan untuk publik supaya setiap individu di perusahaan bisa melihat apa yang sedang dikerjakan yang lain.
Sweet spot OKR itu 0.7; ketika individu mencapai 1.0 artinya performa mereka di atas ekspektasi; ketika individu selalu konsisten dalam pencapaian objektif mereka bisa juga berarti OKRs mereka kurang ambisius jadi mereka perlu melihat goal lebih besar.
Skala rendah harus dilihat sebagai data untuk mempertajam OKRs berikutnya.
OKRs bisa membantu tim dan individu untuk keluar dari zona nyaman, menentukan prioritas kerja dan juga belajar dari kesuksesan atau kegagalan.
OKRs bisa diset setiap bulan, per 3 bulan atau per tahun.
OKRs harus terbuka untuk semua individu, supaya semua orang dan tim punya goal yang sama dan tahu fokus satu dengan lainnya.
Kisah sukses OKRs?
Google, mulai pakai waktu mereka masih tim kecil sekitar 40 orang sampai sekarang walaupun mereka sudah sekitar 70.000 orang. Larry & Sergey mengadopsi karna OKRs itu sejalan dengan prinsip dan keyakinan mereka bahwa setiap individu harus diberi kebebasan untuk set dan mencapai goal mereka — ‘moonshot goals’.
Intel, sebenarnya sudah diadopsi sebelum Google. Intel jadi sukses transisi dari bisnis memory ke microprocessors dan mereka bilang kunci dari kesuksesan transisi ini karna fokus yang didatangkan OKRs.
LinkedIn, ketika Jeff Weiner jadi CEO, bawa OKRs masuk. Dengan OKRs, bukan hanya mereka sukses 20 billion $ IPO tapi juga diakusisi Microsoft. Menurut mereka OKRs itu memberi arah bagi semuanya di perusahaan tentang ‘what really matters’ dan menjadi media komunikasi yang efektif ketika membuat prioritas dan sangat berguna untuk perusahaan yang sedang berkembang.
Oracle, Twitter, Sears and banyak startups lain juga sudah pakai metode goal setting yang agile ini.
Cara kerja OKRs?
Jelaskan timeline, apa yang diharapkan dan apa goal/milestone dan bagaimana akuntabilitas dari setiap individu.
Tentukan timeline
Pilih 3–5 objectives.
Tentukan 3 key results per objective dan skala penilaian.
OKRs itu bisa perpaduan top down dan bottom up, jadi ada komunikasi dari atas ke bawah dan sebaliknya.
Today Google sets annual and quarterly OKRS and holds company-wide meetings quarterly to share and grade OKRs.
- Proven to impact sales and individual performance
Tips for setting objectives:
Pick just three to five objectives — more can lead to over-extended teams and a diffusion of effort.
Avoid expressions that don’t push for new achievements, e.g., “keep hiring,” “maintain market position,” “continue doing X.”
Use expressions that convey endpoints and states, e.g., “climb the mountain,” “eat 5 pies,” “ship feature Y.”
Use tangible, objective, and unambiguous terms. It should be obvious to an observer whether or not an objective has been achieved. Research shows more specific goals can result in higher performance and goal attainment.
Tips for developing key results:
Determine around three key results per objective.
Key results express measurable milestones which, if achieved, will directly advance the objective.
Key results should describe outcomes, not activities. If the KRs include words like “consult,” “help,” “analyze,” “participate,” they’re describing activities. Instead, describe the impact of these activities, e.g., “publish customer service satisfaction levels by March 7th” rather than “assess customer service satisfaction.”
Measurable milestones should include evidence of completion and this evidence should be available, credible, and easily discoverable.
Avoid OKR-writing mistakes
When developing OKRs, try to avoid these traps:
Miscommunicating stretch goal OKRs — Setting stretch goals requires careful communication within the teams delivering the objectives as well as other teams that depend on the work being delivered as part of the stretch goal OKR. If your project depends on another team’s objectives make sure you understand their goal-setting philosophy. If they are using stretch goals you should expect them to deliver on about 70% of their stated OKRs.
Business-as-usual OKRs — OKRs are often written based on what the team believes it can achieve without changing anything they’re currently doing, as opposed to what the team or its customers really want. To test this, stack rank the team’s current work as well as newly requested projects in terms of value versus effort required. If the OKRs contain anything other than top efforts, then they are just business-as-usual OKRs. Drop low-priority efforts and reassign resources to the top OKRs. There are some objectives that will stay the same quarter after quarter, like “Ensure customer satisfaction is over XX%,” and this is ok if that objective is always a high priority. But the key results should evolve to push the team to continue to innovate and become more efficient.
Sandbagging — Teams who can meet all of their OKRs without needing all of their team’s bandwidth may either be hoarding resources, not pushing their teams, or both.
Low-value objectives — OKRs should promise clear business value — otherwise, there’s no reason to expend resources doing them. “Low-value objectives,” even if fully achieved, won’t make much of a difference to the organization. Ask, could the OKR get a 1.0 under reasonable circumstances without providing direct organizational benefit? If so, reword the OKR to focus on the tangible benefit.
Insufficient key results for objectives — If the key results for a given objective don’t represent all that is needed to fully achieve that objective, an unexpected miss on that OKR can happen. That can cause delays of both the discovery of the resource requirements as well as the discovery that the objective will not be completed on schedule.
Develop team OKRs
Although approaches will vary, it can be helpful to commit first to organizational objectives, so that teams and individuals can set their own objectives in service of those larger goals. This can help to create alignment throughout an org. The next decision is how many levels of “team” OKRs work for the organization — does each department, function, and sub-group need OKRs?
For team-level goals, recognize that not every organizational OKR needs to be reflected in every team OKR. It’s possible that a team’s OKRs will focus on just one of the organizational OKRs. But there should be some connection between team OKRs and at least one of the organizational OKRs.
One way to set these team OKRs is to have all of the team leaders meet to set goals. At Google, team leaders sometimes list priorities for the upcoming quarter in the context of the company OKRs. When creating these priorities, it is helpful to pay attention to the organizational OKRs and check:
Do the team priorities connect to any of the organizational key results?
Do the team priorities make it more likely that the organization will successfully achieve the organizational OKRs?
Are there things missing that others think this team should be working on?
Are there more than three priorities?
One thing OKRs are not is a checklist. They are not intended to be a master task list of all the things the teams will work on in a quarter. If a team treats this as a shared to-do list it may result in getting overly prescriptive about what the team wants done, rather than what the team wants to achieve. Use OKRs to define the impact the team wants to see, and let the teams come up with the methods of achieving that impact.
Here are a few sample OKRs a team or individual might set to support an organization’s goal to “reach xx% of industry market share.”
Sample team or individual OKRs:
Objective: Accelerate [product] revenue growth
Key Results:
Launch xx feature to all users
Implement xx initiative to increase revenue per user by xx%
Launch three revenue-specific experiments to learn what drives revenue growth
Secure tech support to build xx feature in Q1
Objective: Improve [product]’s reputation
Key Results:
Re-establish [product]’s leadership by speaking at three industry events
Identify and personally reach out to top xx users
Shorten response time to user-flagged errors by xx%

Keduanya sama-sama bertujuan untuk merencanakan target dalam jangka waktu tertentu, tapi ada beberapa aspek pada OKRyang tidak terdapat dalam KPI.
Agar lebih memahami mekanismenya, berikut adalah perbedaan KPI dan OKR serta tahap-tahap yang perlu dilakukan untuk menyusun OKR.
Perbedaan OKR dan KPI
KPI atau Key Performance Indicatorsmerupakan metrik kinerja yang digunakan untuk mengevaluasi keberhasilan suatu organisasi tertentu.
KPI dapat diterapkan untuk program, proyek, produk, maupun bentuk lainnya. Menggunakan KPI, perusahaan dapat mengukur keberhasilan penjualan hingga pertumbuhan media sosial.
Beberapa perusahaan seringkali menerapkan KPI yang digunakan oleh perusahaan lain sebagai indikator keberhasilannya. Padahal, ini merupakan tindakan yang keliru karena setiap perusahaan memiliki tujuan spesifik yang berbeda. Dampaknya, KPI yang ditetapkan justru tidak tercapai.
Berbeda dengan KPI, Objectives and Key Results (OKR) menggambarkan tujuan tim dan perusahaan, serta key results yang menunjukkan sejauh apa tujuan telah tercapai. OKR mengandung tujuan yang lebih spesifik dan disertai langkah-langkah terukur untuk mencapai tujuan tersebut.
OKR tidak hanya diberikan dalam tingkat perusahaan, tapi juga tim hingga perorangan. Tujuan yang tertera pada OKR biasanya memiliki jangka waktu selama tiga bulan hingga satu tahun. Metode ini diadopsi dari teknik perencanaan yang diterapkan oleh Intel dan Google.
Cara menyusun OKR
OKR adalah metode penilaian kinerja yang telah berhasil diterapkan oleh berbagai perusahaan besar. Tertarik untuk menggunakannya? Berikut ini adalah sejumlah langkah yang perlu dilakukan untuk menyusun indikator keberhasilan ini.
1. Pilih tool yang akan digunakan
Setelah memastikan bahwa semua orang yang terlibat dalam perusahaan memiliki pemahaman tentang OKR, pilihlah tool yang akan digunakan. Tool yang dimaksud dapat berupa spreadsheet sederhana hingga software khusus.
Apa pun jenis tool yang digunakan, pastikan bahwa semua orang memiliki akses yang mudah untuk memantau, mengikuti, dan mengelola OKR-nya masing-masing. Pengelola OKR juga perlu memiliki akses terhadap OKR yang telah dipenuhi maupun yang akan datang.
2. Merancang OKR
Saat merancang OKR, ada dua pertanyaan utama yang menjadi acuan, yaitu:
- Apa tujuan yang harus dicapai?
- Bagaimana cara mencapai tujuan tersebut?
Tujuan yang ditetapkan pada pertanyaan yang pertama idealnya konkret dan ambisius. Namun, perusahaan harus menjaganya tetap realistis melalui langkah-langkah yang menjadi jawaban dari pertanyaan kedua. Semua langkah tersebut harus dapat diukur.
Penyusunan OKR harus melibatkan semua pihak tanpa adanya dikte maupun mandat dari pihak tertentu. Setiap level jabatan harus menentukan tidak lebih dari 5 tujuan utama yang terdiri dari maksimum 4 hasil kunci. Jangka waktunya dapat beragam, tergantung kesepakatan dalam perusahaan.
3. Menyusun OKR perusahaan
OKR perusahaan biasanya disusun oleh para CEO atau orang-orang pada kursi kepemimpinan tertinggi karena mereka memahami hal terpenting yang dibutuhkan perusahaan. OKR pada level ini merupakan gambaran besar yang mewakili seluruh perusahaan.
4. Menyusun OKR tim
OKR tim disusun dalam dua tahap. Tahap pertama melibatkan manajer dengan CEO atau pimpinan tertinggi untuk menyusun rancangan OKR. Kemudian, manajer mendiskusikan rancangan OKR bersama anggota tim dalam tahap selanjutnya. OKR tim harus menggambarkan prioritas tim tersebut dan bukan perorangan.
5. Menyusun OKR perorangan
OKR perorangan menunjukkan berbagai hal yang perlu dikerjakan oleh masing-masing anggota tim. Setiap anggota tim harus memenuhi tugas-tugas yang tertera pada OKR perorangan dalam batas waktu yang telah ditentukan. Dari sinilah manajer dapat memantau kemajuan anggota timnya.
6. Mengevaluasi OKR
Perusahaan harus mengevaluasi OKR untuk mengetahui sejauh apa tujuan telah tercapai. Pada umumnya, pencapaian yang sukses berada pada rentang 60-70%. Persentase pencapaian kurang dari rentang tersebut belum tentu menandakan kegagalan, melainkan target yang hendak dicapai terlampau tinggi.
Sebaliknya, persentase keberhasilan OKR yang selalu mencapai 100% dapat menandakan bahwa target perusahaan kurang ambisius. Jika demikian, maka perusahaan perlu menilai kembali target yang hendak dicapai untuk jangka waktu berikutnya
What Are OKRs? How to Use OKRs for Planning (and Achieving) Your Goals
How did Google grow from 40 to 88,000 employees and $100+ billion in global revenue? Sure, their killer products, ubiquitous search engine, and cloud services played a huge role. But they also had a not-so-secret, secret weapon at their disposal: OKRs.
First developed by legendary Intel CEO Andy Grove, Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) is a collaborative goal-setting system that was adopted by Google in 1999. Since then, OKRs have helped Google (and countless other companies) not just build products rapidly, but also stay focused, engaged, and aligned with their company goals.
OKRs translate your company strategy into a digestible way that allows every team member to know they’re working on the right thing.
Even better, OKRs are dead simple. At least in theory.
In practice, there are a few best practices and pitfalls you need to watch out for if you want to get the most out of bringing OKRs to your business.
So, if you’re tired of hitting the finish line only to realize you were working toward the wrong goals, sick of feeling like the work you do each day isn’t moving the needle, and want to get your team more aligned with company goals and strategy, OKRs are for you.
In this guide, we’re going to run you through everything you need to know about OKRs. From what exactly they are, to clear examples, tips for writing them, and how to implement them at your company. Sound good? Let’s get started.
What are OKRs?
Like their name implies, OKRs are made up of two distinct parts:
- Objectives: What you want to accomplish
- Key Results: How you’re going to measure the success of your work
Sounds simple, right? On their own, an Objective and Key Results are easy concepts to understand. But it’s when you bring them together that magic happens. To clarify what we’re talking about, let’s tell a little story:
Way back in the early days of Google, venture capitalist John Doerr paid a visit to the company’s Mountain View HQ to talk about their future.
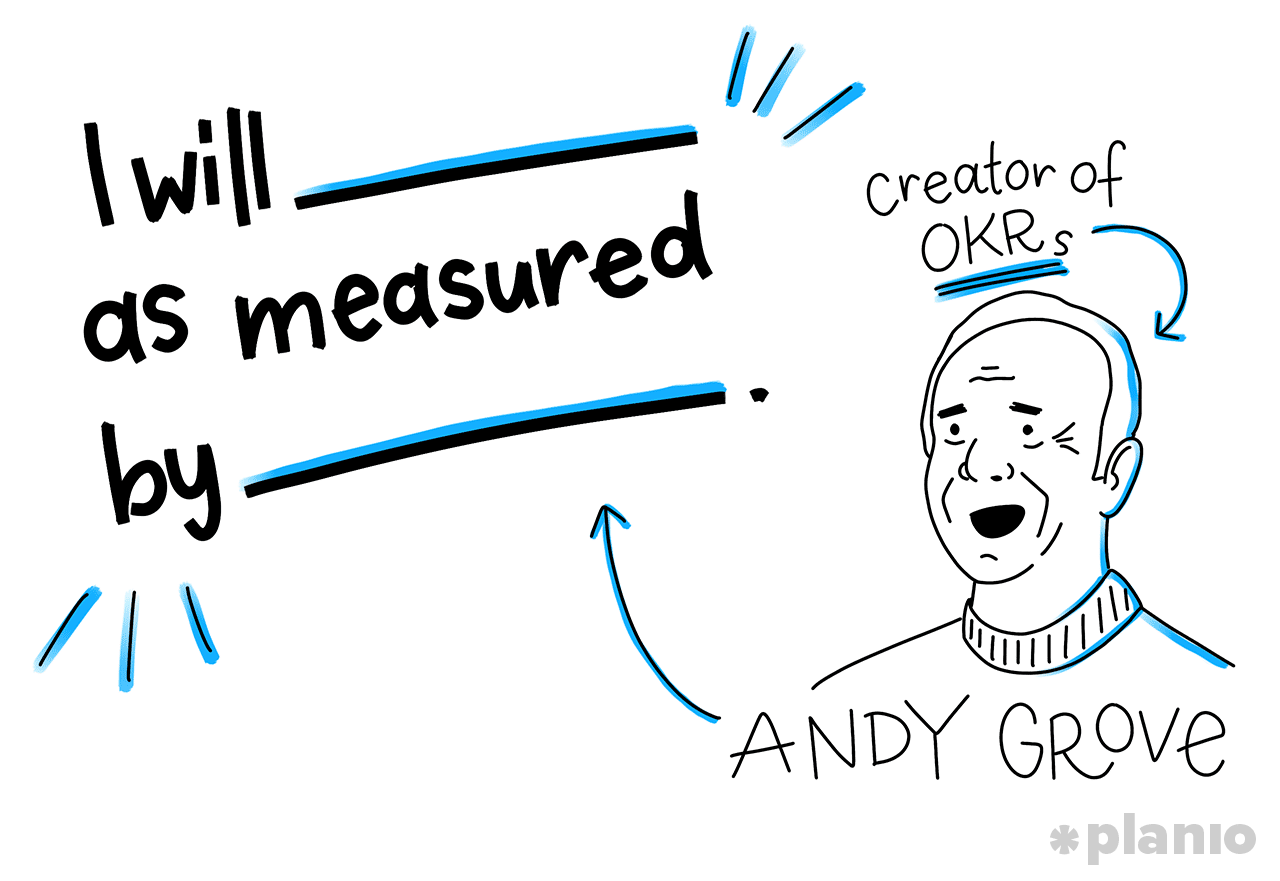
Doerr had previously worked under Andy Grove at Intel (the creator of OKRs) and had joined just as Intel was transitioning from a memory company to a microprocessor company. A pivot is no small feat for any company. But one the size of Intel? To keep all of their teams in line as they went through these changes, Grove came up with the idea of OKRs, which he described through a simple formula:
I will _________ as measured by _________.
That formula was what kept Intel in check as they successfully changed their business model. And it was what Doerr wanted to show the founding team at Google.
If you think about it, a proper goal isn’t just a statement of what you want to achieve, but a road map of how you’re going to get there. The “as measured by” in Grove’s formula is what makes a goal a goal (otherwise you just have an aspiration).
This formula is the best way to describe what an OKR really is:
I will (Objective) as measured by (Key Results).
In this context, we can expand the definitions of each part of the OKR to something like:
- Objectives: Memorable, qualitative descriptions of what you want to accomplish in a given time-frame (such as quarterly). Objectives should be ambitious and feel somewhat uncomfortable. They should also be short, inspirational, and public so everyone knows what everyone else is working on.
- Key Results: A set of 2–5 metrics that measure your progress towards the Objective. They should describe an outcome, not an activity (i.e. they shouldn’t include words like “help”, “consult”, or “analyze”). Once they are all completed, the objective is necessarily achieved.
The power of OKRs, as Doerr describes, is in having a “North Star” every quarter by which you can set your priorities. As well as being able to see how it fits in with everyone else’s goals and priorities:
“It was incredibly powerful for me to see Andy’s OKRs, my manager’s OKRs, and the OKRs for my peers. I was quickly able to tie my work directly to the company’s goals. I kept my OKRs pinned up in my office and I wrote new OKRs every quarter, and the system has stayed with me ever since.”
Instead of simply being another task on your list, an OKR is an ambitious goal that’s supported by concrete actions that you need to take to hit. As Google explains on their re:Work blog, Key Results should be numerically based and easy to grade with a number (they use a scale of 0 – 1) with the “Sweet spot” for OKR success being somewhere around 60—70%.
If someone consistently fully attains their objectives, their OKRs aren’t ambitious enough and they need to think bigger.
When used this way, OKRs enable teams to focus on the big ideas and accomplish more than they thought was possible. All without the usual fear of the repercussions of “missing” a goal.
It might seem strange to purposefully set goals you don’t think you’ll hit. But when aiming high, even failed goals result in substantial progress. This is where the nuances and skills behind writing a good OKR becomes apparent.
What is an example of a good OKR?
So what does this all look like in practice? Let’s run through an OKR example to solidify our understanding of their fundamentals before moving on.
Let’s say your business, like many others, relies on giving a better customer experience than your competitors.
So, your quarterly objective might be something along the lines of “create an awesome customer experience”. But how do you know if you’re succeeding in doing this?
You need some form of measurement to make this an OKR you can actually work towards. But what shows you’re creating an “awesome” customer experience?
For one, you could look at your NPS, or Net Promoter Score (a tool that can measure what people think of your brand) as well as your customer churn rate (how many customers you’re losing a month).
A great experience would mean people both say nice things about you and stick around.
Sounds good? But it’s not the full story.
Before we get going, let’s think about these Key Results for a second. By saying we want to improve our NPS score and lower churn, it sounds like we’re willing to do whatever it takes to make our customers happy. But to run a sustainable business, we need to keep costs under control. Which is why we should add a third Key Result around cost as a countermeasure.
So, that OKR would look like:
Objective: Create an awesome customer experience
Key Results:
- Improve Net Promoter Score from X to Y
- Reduce Monthly Churn Rate to X%
- Maintain Customer Acquisition Cost of under $X
Now we have an ambitious objective aligned with our company’s strategic goals and a small number of measurable key results that will tell us if we’re doing the right things to get there.
At the end of the work period (typically a quarter), your OKRs provide a reference of how well you did, where you succeeded, and where you need to focus more attention in the future.
Real life example: Uber’s OKRs
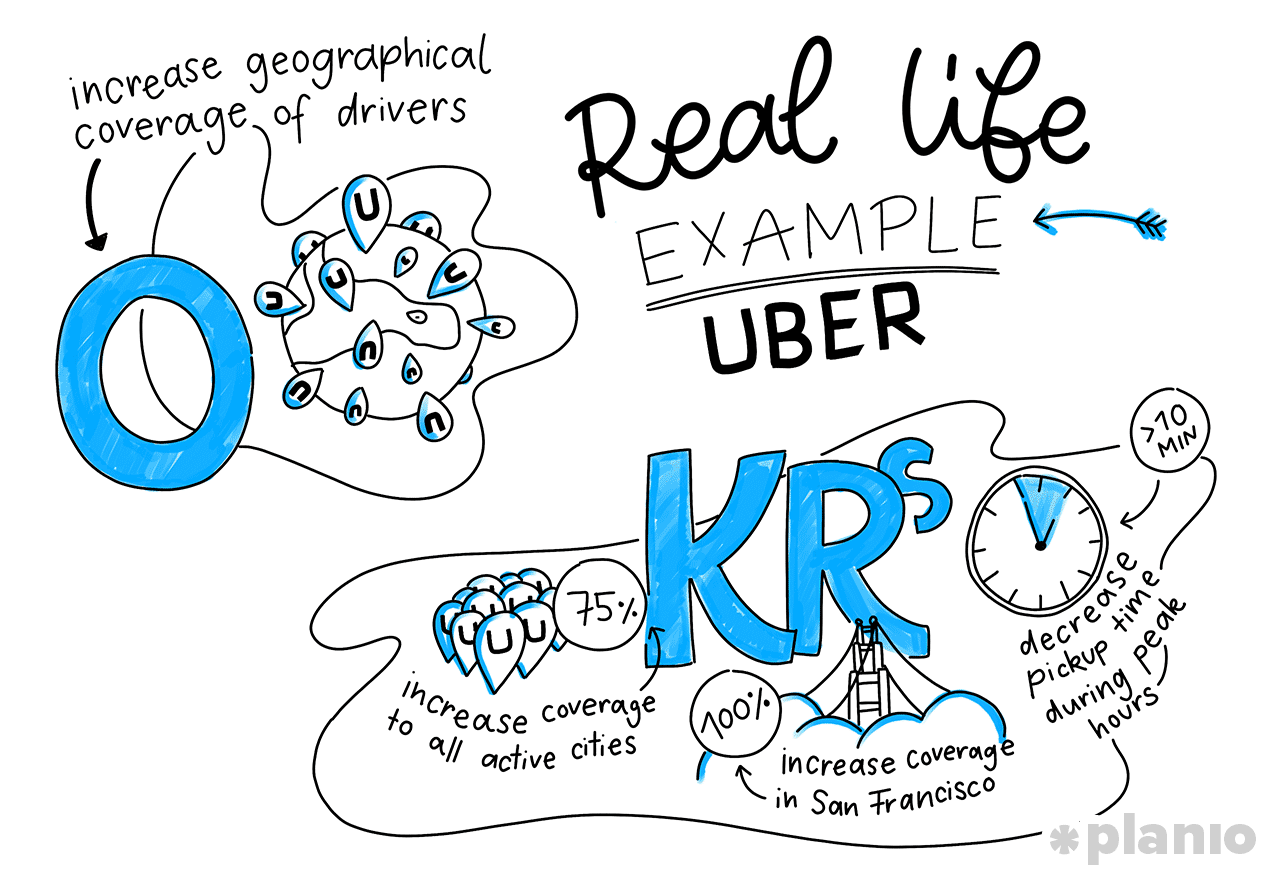
Here’s another OKR example shared by former Google employee Niket Desai, where he explains how Uber might use OKRs to work towards their ultimate company goal of being the most readily available ride-sharing service in the world:
Objective 1: Increase Drivers in the Uber System
Key Results:
- Increase driver base in each region by 20%
- Increase driver average session to 26 hours/weekly in all active regions
Objective 2: Increase geographical coverage of drivers
Key Results:
- Increase coverage in San Francisco to 100%
- Increase coverage for all active cities to 75%
- Decrease pickup time to <10min in any coverage area during peak hours
Solving how to meet these OKRs is up to the team. But as Desai shows in this example, a good OKR helps align them with company strategy and gives them a pretty clear roadmap of how to get there.
Best practices for writing good OKRs
The above examples should give you a good idea of how to write good OKRs. But if you’re still unsure when you try to use them in your own business, here’s a few questions you can run through:
Does the OKR align with my company’s main business strategy and goals? Once the organization knows what it’s focused on and how it will measure success, it’s easier for individual team members to connect their projects with the company objectives.
Is the objective supported by everyone at the company? Once everyone agrees what the most important objectives are, it can be easier to say no to the less important ideas. With OKRs, saying no isn’t a political or emotional debate. It becomes a rational response to a commitment that the entire organization has already made.
Is the OKR adaptable and agile? OKRs are ambitious because they want to leave room for experimentation and growth. If you’re too committed to a single path to success, you might be limiting your team’s creativity and missing out on big opportunities. Remember to make sure your Key Results are adaptable and agile enough that they can be completed in many ways.
Does it have a clear deadline? OKRs can be incredibly motivating. As long as they have a strict time frame. Set a strong deadline and then check in weekly, monthly, or quarterly on progress (whatever works for your team and your communication style.)
Are your Key Results measurable and progress-based? Can you put a numerical value on the result you want to see? If not, you don’t have a good Key Result.
Is it aspirational? Does your OKR get your team excited? Can you set them off towards a moonshot idea where even moving the needle a bit can be seen as success? With OKRs, the goal isn’t to always hit 100%. Make sure you’re pushing your team while staying within the bounds of what’s realistic.
If your OKRs aren’t ticking all of those boxes, you might want to spend some more time with them before hitting “go”. It’s always worth it to spend more time upfront devising the best possible OKRs than to send people down the wrong path.
How are OKRs different from other goal-setting exercises? Are there upsides and downsides I should be aware of?
OKRs are a powerful tool. But they’re not a silver bullet for goal setting. Every methodology has its upsides and downsides and OKRs are no different. What makes OKRs different is that they’re not simply just a way to set goals.
OKRs communicate strategy and priorities from the highest level right down to each individual team member.
They allow team leaders to push groups in the right direction while giving them constraints to make sure work gets done. They’re fantastic tools not just for moving the needle, but for focus, prioritization, and clear communication (some of the biggest issues facing most businesses today!) On top of that, OKRs are special in a number of other ways:
- They’re simple: OKRs are pretty simple to understand and make day-to-day tasks easier as everyone knows what they’re working towards. They help you reduce the time spent setting goals so you can work more on achieving them (not analyzing them).
- They’re agile: By working in short cycles and with clear goals, OKRs let you measure the work you’re doing, see how it’s stacking up against company-wide goals, and adjust your approach on a regular basis.
- They bring a level of transparency: As we just said, OKRs are a form of communication. At Google, all OKRs are public from the CEO down, which means at any time you can see how the people that work around you are helping the company’s cause.
- They help workers find meaning and purpose: Studies have shown that feeling a connection and purpose in the work you do makes us happier, more productive, and more motivated to work. By showing your team how the work they do is tied into the company’s goals you’re helping give them the purpose they need to push forward.
- They’re the link between strategy and tactics: Rather than having a lofty company mission with no way to know if you’re getting there. OKRs let you choose tactical objectives that work towards your overall goal.
However, there are also a few potential downsides you should understand before adopting OKRs:
- You need to know where your company is headed: As Andy Grove wrote in High Output Management: “The absolute truth is that if you don’t know what you want, you won’t get it.” OKRs help you move forward quickly and if you’re not pointing people in the right direction, or your teams aren’t aligned, they can do harm rather than good.
- You need to commit the time to planning proper OKRs: Just because OKRs can be simple, doesn’t mean they’re easy. Team leaders and founders are busy. You’re hiring, strategizing, and putting out fires. But the success of OKRs depends on putting in the proper time to plan and strategize what they should be.
- You need a good understanding of how success IS measured: Again, that “M” word comes up. If you don’t know what success looks like and the right metrics to tell you if you’re reaching it, there’s no point in trying to use OKRs.
What it all comes down to is that OKRs work well when you have a clear strategy and know where your company is headed.
Like any goal-setting exercise, the more you know about the final destination, the better chance you’ll actually get there.
How to adopt OKRs for your company
Bringing OKRs to your company isn’t just a matter of copying the way a company like Google uses them. Google isn’t the average company, and they’ve spent almost 2 decades growing, scaling, and experimenting with how their internal goal-setting structure works. Because of that, how they use OKRs will be incredibly different than how you will.
That’s because at its core, OKR isn’t a methodology. There’s no set path or steps you take for bringing it into your workplace. Instead, it’s a set of practices and ideals that you should understand and customize for your teams.
If you want to start experimenting with OKRs, however, there are a few best practices you should follow:
Start small and iterate
According to OKR coach Felipe Castro, it’s important to understand the tradeoffs you’re making when you adopt OKR. Which means it’s probably a good idea to start small and iterate as you understand how it works in your company.
In Google’s own guide to introducing OKRs, they suggest starting with the basics:
- What are OKRs? Explain the basics of OKRs to your team and how they work.
- Why use OKRs? Review your current approach to goal-setting and any limits or issues you’ve had with that approach. This is a good time to highlight how OKRs connect everyone’s work to the company’s purpose and mission.
- How do OKRs work? Explain the timeline of your OKR cycle (it’s good to start with shorter ones. Around 30-45 days.) What is expected of each person. What the major milestones will be. And what success looks like. Remember, you’re not shooting for 100% every single time. And it might take some time to get your team to accept that 60-70% is totally fine.
Focus on communication and prioritization
One of the most important aspects of OKRs is that they’re public. Which isn’t always an easy thing for teams to do. However, making it clear where you can see what other people are working on and what metrics they’re chasing is an important part of adopting OKRs.
As former Googler and former Twitter CEO Dick Costolo explains:
As you grow a company, the single hardest thing to scale is communication. It’s remarkably difficult. OKRs are a great way to make sure everyone understands how you’re going to measure success and strategy.
Use regular check-ins to stay disciplined
Because of the Agile nature of OKRs, it’s important to set and stick to regular check-ins. And that doesn’t just mean at the start and end of an OKR cycle. You might want to set a cadence that includes:
- OKR planning sessions: Bring together a small group of people that work together to plan and talk through objectives and key results for the next cycle.
- Weekly check-ins: A team-level meetingfocused on tactical updates to ensure everyone is working on the right priorities and isn’t being blocked.
- Mid-quarter/cycle review: A quick step back to reassess the OKR, add or eliminate Key Results or adjust targets, and define action plans for addressing OKRs that are below your goal.
- All-hands meetings: A company wide meeting where you can communicate and reiterate your strategy and goals to make sure everyone’s still aligned and excited.
Learn how to run meetings that won’t suck the life out of your team with our free Guide to Running Fast and Efficient Meetings.
Don’t go all in on OKRs until your whole company is ready
Change is hard. And it’s probably not a good idea to just drop OKRs on your entire team. Instead, choose to either integrate them horizontally or vertically:
- Horizontal: Start with one team and add additional ones each cycle or quarter.
- Vertical: Start with company OKRs and senior management and then add new layers beneath each cycle or quarter.
The most common mistakes teams make with OKRs
How your company handles OKR will be unique to you. And the more you add them and work with them, the better you’ll be at aligning your teams and measuring results. However, early on in your path to adopting OKRs there are some common pitfalls you should watch out for:
Miscommunicating “Stretch Goals”
At Google, OKRs are used to go after stretch goals. Or, goals they don’t necessarily think they can hit. And while this is a fantastic way to motivate your team to look for unique and innovative solutions, if not communicated properly it can cause some serious headaches.
Once OKRs have been adopted across multiple teams, you’ll need to be very aware of the other team’s goal-setting philosophy. If part of your project depends on another team’s Objectives, make sure you know whether they’re most likely to deliver you something at 95% or 65% of their stated OKR.
“Business-as-usual” OKRs
If your current goal-setting philosophy is to be conservative with what you’re going after, this isn’t going to jive with OKRs. To test this, look at your team’s current work as well as requested projects and rank them in terms of value versus effort required. If the OKRs you’ve chosen have anything other than top effort tasks you should drop them and re-assign the resources.
Of course, there are some Objectives that will stay the same each cycle (especially around maintenance or upkeep). This is ok as long as the Objective is high priority and brings in business value. But always try to make sure your Key Results push the team to evolve and look for new ways to be more efficient.
“Sandbagging”
If a team is consistently hitting their OKRs without using all their bandwidth, they may be hoarding resources or not pushing their team (or both). This can kill the morale of other teams who are going after stretch goals. Make sure you have a consistent, company wide philosophy around how difficult Objectives should be and what success looks like.
Not enough Key Results for an Objective (i.e. a lack of clarity)
We can’t say enough how the OKR secret sauce comes down to measurement. And if the Key Results for an Objective don’t represent everything that’s needed to fully achieve it, you’re not setting your team up for success. Take the time during the planning phase to determine exactly what that objective needs to be successful.
The way you set goals says a lot about your company. Are you concerned with just getting through the day? Or are you looking 10 years down the road?
With OKRs you can do both. OKRs not only help you communicate the big vision stuff that builds behemoths like Google and Twitter. They also make sure every person doing their daily work and putting out fires is in alignment.
But they take work. As John Doerr wrote in Wired:
OKRs are not a silver bullet. They cannot substitute for sound judgment, strong leadership, or a creative workplace culture. But if those fundamentals are in place, OKRs can guide you to the mountaintop.
It doesn’t matter how quickly your company grows if it’s going in the wrong direction. But if you do the work upfront to dial in your strategy and vision, OKRs can be the superfuel you need to blow past your goals.
Mau nonton video penggunaan OKRs di Google?
Langsung saja lihat presentasi Rick Klau di Google Venture.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar